Request a demo specialized to your need.
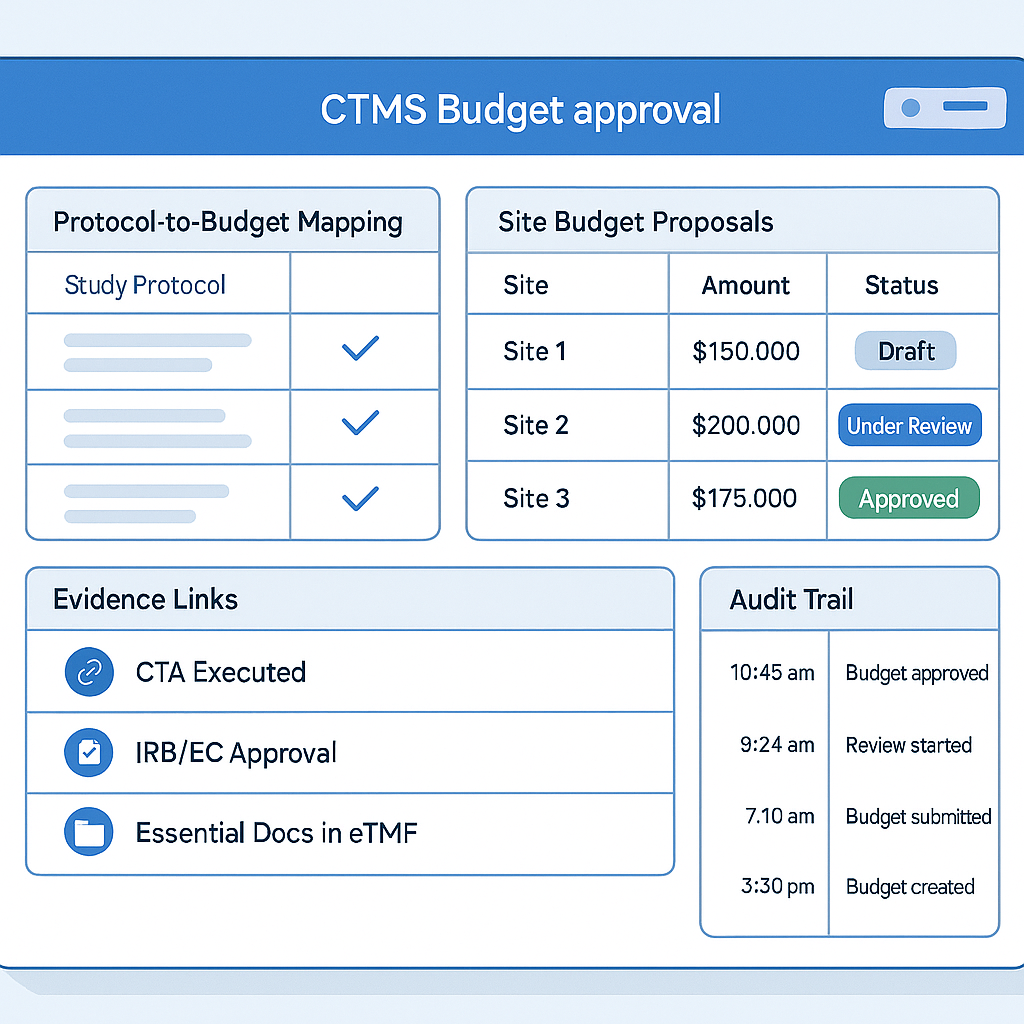
Design CTMS budget approvals that are fast, explainable, and compliant.
Site budgets are the financial backbone of every clinical trial. They define how investigators are compensated, how sites are incentivized to enroll and retain subjects, and how sponsors control one of the largest cost components of a study. Yet in many organizations, site budget approvals remain document-driven, static, and disconnected from actual trial execution.
Budgets are negotiated upfront, approved in bulk, locked into spreadsheets or contract PDFs, and only revisited when problems surface—overpayments, missed milestones, enrollment delays, or audit findings. This static approach is increasingly incompatible with modern clinical trials that are adaptive, global, decentralized, and data-rich.
Event-Driven Site Budget Approvals represent a paradigm shift. By linking budget approvals directly to real clinical and operational events inside the CTMS, organizations can move from periodic, manual budget governance to continuous, evidence-based financial control.
The Problem with Traditional Site Budget Approvals
In a traditional model, site budget approvals typically suffer from four structural weaknesses:
-
Time-based approvals instead of activity-based approvals
Payments are approved monthly or quarterly, regardless of what actually happened at the site. -
Limited traceability to protocol events
It is often difficult to prove that a payment corresponds to a specific visit, procedure, or milestone. -
Manual coordination across systems
CTMS tracks visits, contracts define terms, finance systems process payments—but approvals sit outside all three. -
Reactive exception handling
Deviations are found after payments are made, requiring clawbacks, adjustments, and audit justifications.
As trial complexity increases, this model creates unnecessary friction between Clinical Operations, Site Payments, Finance, and Compliance teams.
What Does “Event-Driven” Mean in a CTMS Context?
Event-Driven Site Budget Approvals shift the approval trigger from calendar dates and invoices to verified clinical and operational events captured in the CTMS.
An “event” can include:
-
Subject visit completion (e.g., Screening, Baseline, Visit 3)
-
Procedure completion (e.g., imaging, lab draw, device implantation)
-
Enrollment milestones (first patient in, nth patient enrolled)
-
Study milestones (site activation, close-out readiness)
-
Protocol-driven exceptions (unscheduled visits, reconsents)
Each event becomes a financial signal—automatically initiating budget validation, approval workflows, and downstream payment readiness.
How Event-Driven Budget Approvals Work
At a high level, the model operates as follows:
-
Protocol & Contract Intelligence
Budget line items are structured and mapped to protocol events (per-visit, per-procedure, milestone-based). -
Event Capture in CTMS
As CRAs, site staff, or integrations record events in CTMS, those events become system-verifiable triggers. -
Automated Budget Validation
The system validates:-
Is the event billable?
-
Is it within the approved contract version?
-
Are caps, holdbacks, or conditional rules satisfied?
-
-
Policy-Driven Approvals
Based on amount, risk, or exception status, approvals may be:-
Auto-approved
-
Routed to Clinical Ops, Finance, or Study Management
-
Flagged for exception review
-
-
Audit-Ready Execution
Every approval is tied to:-
The underlying CTMS event
-
The applicable budget and contract version
-
The approver, timestamp, and rationale
-
This creates a closed-loop, inspection-ready financial workflow.
Key Advantages of Event-Driven Budget Approvals
1. Financial Accuracy Aligned to Reality
Payments reflect what actually happened, not what was assumed to happen. This dramatically reduces overpayments, missed payments, and disputes with sites.
2. Faster Site Payments, Higher Site Satisfaction
When approvals are triggered automatically by verified events, sites are paid faster—without waiting for batch reviews or manual reconciliations.
3. Continuous Budget Control
Sponsors gain real-time visibility into:
-
Budget burn by site and country
-
Remaining obligations by visit and milestone
-
Forecasted spend based on enrollment velocity
4. Built-In Compliance & Audit Readiness
Every payment decision is traceable to protocol execution, contract terms, and approval policies—critical for inspections and financial audits.
Event-Driven Approvals and the Rise of Continuous Financial Governance
Event-driven budget approvals are a cornerstone of Continuous Controls Monitoring (CCM) in clinical trial financials. Instead of reviewing spend after the fact, controls operate continuously:
-
Blocking payments that exceed contract caps
-
Flagging out-of-window visits
-
Enforcing approval thresholds dynamically
-
Ensuring segregation of duties in approval paths
This transforms CTMS from a tracking system into a financial governance engine.
The Role of Automation and AI
As trials scale, automation and AI enhance event-driven approvals in powerful ways:
-
AI-assisted anomaly detection to identify unusual site billing patterns
-
Predictive spend analytics based on enrollment and visit trends
-
Natural language explanations of why a payment was approved or flagged
-
Adaptive rules that adjust approval rigor based on site risk profiles
Over time, systems evolve from rule-based automation to intelligent financial orchestration.
Why Platform Architecture Matters
Event-driven approvals cannot be bolted onto disconnected systems. They require a CTMS platform that is:
-
Process-unified across CTMS, contracts, budgets, and payments
-
Event-native, where protocol activities are first-class data objects
-
Workflow-centric, with configurable approval logic
-
Audit-grade, supporting electronic signatures and immutable logs
This is why modern, platform-based CTMS solutions—such as those delivered by Cloudbyz—are increasingly embedding event-driven financial workflows directly into CTMS and Clinical Trial Financial Management (CTFM).
Looking Ahead: From Event-Driven to Outcome-Driven
The future of site budget governance will move beyond individual events to outcome-driven models, where:
-
Quality metrics influence payment timing
-
Enrollment performance dynamically adjusts incentives
-
Risk signals trigger tighter approval controls
-
Financial decisions align directly with trial outcomes
Event-driven approvals are the foundation for this next generation of adaptive, intelligent trial finance.
Closing Thought
Event-Driven Site Budget Approvals fundamentally change the relationship between clinical execution and financial governance. By anchoring approvals to real trial events, organizations gain speed without sacrificing control, transparency without added overhead, and compliance without constant firefighting.
In a world where trials are increasingly complex and margins are under pressure, this approach is not just innovative—it is inevitable.
Subscribe to our Newsletter

